| Radioactivity for Dummies | ||
| Who discovered radioactivity? | ||
| What? | Who?? | When? | Parts | Decay | Links | Goof | Plants | ||
Natural radioactivity was first observed in 1896 by Antoine Henri Becquerel. He discovered that when salts of uranium are brought into the vicinity of an unexposed photographic plate carefully protected from light, the plate becomes exposed. The radiation from uranium salts also caused a charged electroscope to discharge. In addition, the salts exhibit phosphorescence and are able to produce fluorescence. Since these effects are produced both by salts and pure uranium, radioactivity must be a property of the element and not of the salt.  In 1899, Ernest Rutherford discovered and named alpha and beta radiation. Rutherford discovered that at least two components are present in the radioactive radiations: alpha particles and beta particles. Subsequent experiments in which radiations were subjected to magnetic and electric fields revealed the presence of a thrid component, gamma rays. In 1899, the discovery of the radioactive gas radon was made by Rutherford and Frederick Soddy. They observed that radon was in association with thorium, actinium, and radium. In 1911, Rutherford proved the existence of a nucleus within the atom by experiments in which alpha particles were scattered by thin metal foils. In 1900 P. Villard identified gamma radiation. 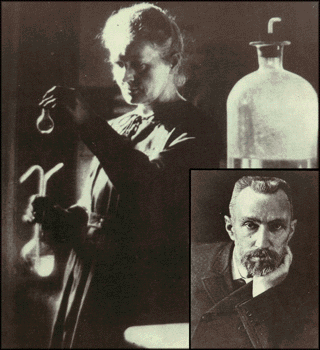 Marie and Pierre Curie, French chemists, extended the work on radioactivity, demonstrating the radioactive properties of thorium and descovering the highly radioactive element radium in 1989. They deduced that radioactivity is a phenomenon associated with atoms, independent of their physical or chemical state. The uranium-containing ore pitchblend is more intensely radioactive than the uranium salts that were used by Becquerel. That means that there must be radioactive element in the ore. They carried through a series of chemical treatment of the pitchblende that resulted in the discovery of two new radioactive elements, polonium and radium. Marie Curie also discovered that the element thorium is radioactive and in 1899, the radioactive element actinium was discovered by Andre Louis Debierne, also a french chemist.  Frederic and Irene Joliot-Curie discovered the first example of artificial radioactivity in 1934 by bombarding nonradioactive elements with alpha particles. |
||
|
Enter content here |
||
|
Enter supporting content here |