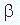
|
||||||
| Three Fundamental Parts |
|
The radiation produced during radioactivity is predonminantly of three types. Those types are alpha, beta, and gamma. These types differ in velocity, the way in which they are affected by a magnetic field, and in their ability to penetrate through matter.
FYI: The number below a paragraph of text is the number of the line in the works cited. Clicking on the link below the text will take you to the works cited page. Then scroll down to the number that corresponds to the number below the paragraph. Clicking on the link on the works cited page will take you to the cite on the net in which I received the information. |
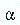 Alpha Radiation
Alpha rays have the least penetrating power. They also move at a slower velocity than beta or gamma rays. Alpha rays are deflected slightly by a magnetic field in a direction that indicated a positive charge.
Alpha particles penetrate into aluminum only a few thousandths of a centimeter. These particles are deflected toward the negative electric pole. Alpha particles are positively charged and are heavier than beta particles. An alpha particle is a doubly charged helium ion that consists of two neutrons and two protons. They can be emitted only from the nucleus of an atom. Loss of an alpha particle by a nucleus results inthe formation of a new nucleus that is lighter than the original by four mass units. Alpha Decay Alpha decay reduces the atomic weight of a nucleus. The net effect of alpha radiation and decay is to produce nuclei that is lighter than the original radioactive substance.
|
|
|